Informit Search | DOI (Digital Object Identifier)
Information for Publishers
What is a Digital Object Identifier (DOI)?
- A DOI is a code that is assigned to a digitally published resource, such as a journal article or conference paper. The DOI consists of numbers, punctuation and letters and may include a letter code that corresponds to the name of the journal.
- Selecting the DOI or pasting the DOI into a search engine should take you straight to the article.
- DOIs are assigned to the content during publication by the publisher (not by Informit).
Why should publishers assign DOIs to their publications?
- A DOI makes content more discoverable
- Reduces confusion between items with similar titles.
- A reliable link directly to the publication benefits publishers, authors and researchers.
How do publishers create and add DOIs to publications?
- Publishers assign DOIs by applying construction principles. See this guide from CrossRef for DOI syntax: Constructing your DOIs - Crossref
- Primary source documents on publisher websites must display DOIs according to DOI display guidelines
- DOIs are always displayed on the first page or title page of the book or report or on the first page of the chapter, conference paper or article, as in the below example.
- DOIs for individual papers, chapters or articles may also be displayed in the Table of Contents for that journal issue, conference, report or book.

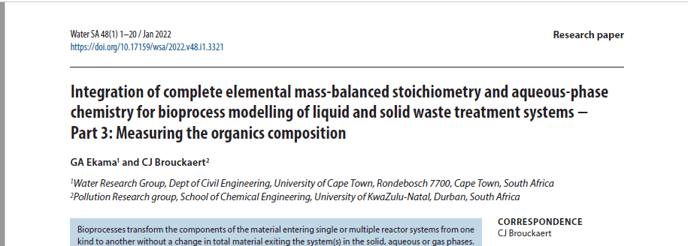
- The DOI, in the above example, starts with the numbers after the second slash: 10.17159/wsa/2022.v48.i1.3321
- DOIs are always assigned from a range already allotted by a DOI registration agency.
How are DOIs registered?
- DOI registration agencies handle processes for a range of publishers.
- Publishers should keep their registered DOIs updated so the links still work if they move content around within their website or change to a new website.
Do DOIs work if the target website changes?
- DOIs should always resolve to the web page that is registered by the publisher. If the publisher moves content around, they must update the addresses registered via their DOI agency.
- There should be no broken links. If searchers follow a DOI link that fails to resolve, they are directed to a centralised form for reporting the problem.
How does Informit handle DOIs in metadata records?
- Informit includes DOIs in metadata records wherever they are supplied by publishers.
- A DOI link within an Informit record resolves to the primary source website. This target page may be the primary resource or a preliminary “landing page.”
- Publishers should alert Informit of policy changes to adding DOIs to publications so that the DOIs are included in all relevant Informit records.
Why do links to Informit records contain “doi”?
- Informit URLs look like DOIs as they have “doi” in the string, but these are not DOIs and are not registered as such.
- The Informit syntax for record locations is:
[domain]/doi/[publisher code]/[product code].[document number]
e.g. https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.252862385381350
Helpful links
Still Need Help?
If you have further questions on how to save searches, please reach out to support.informit@rmit.edu.au.
